The ability of the body to use insulin, which is important for metabolic health, and how the body uses glucose and manages energy, can be influenced by physical activity. Recent studies reveal that the strength and timing of exercise play key roles in deciding levels of this sensitivity to insulin. With more people facing issues with insulin resistance, especially those leading inactive lives, it's crucial to understand these factors. This article will look into the effects of how strong and when we exercise influence insulin sensitivity. It offers an understanding of how to best set up physical activity for superior health results.
Insulin is a hormone that the pancreas makes. It helps take glucose from your blood to use for energy in cells. If insulin sensitivity is good, your body can use insulin well and manage glucose effectively. But if this sensitivity goes down, then the cells of your body don't react as much to insulin and it leads to higher levels of sugar in the blood. This state, identified as insulin resistance, is a major risk aspect for type 2 diabetes and other metabolic problems. Paying attention to insulin sensitivity by altering lifestyle habits, especially through physical activity, can deeply influence general health.

The power of physical activity shows how much effort the body puts in during exercise. Workouts with more intensity, like high-intensity interval training (HIIT), are becoming popular because they may improve insulin sensitivity. Research points out that doing intense physical activities can greatly boost insulin sensitivity, even just after a short time of exercising. This is because the body needs more metabolism when doing intense workouts, which makes muscles take in glucose better and enhances overall metabolic wellness. On the other hand, exercises of medium intensity are indeed helpful but may not make insulin sensitivity improve as fast as high-intensity training does.
Exercise time can affect insulin sensitivity, according to studies. The research indicates different effects on glucose metabolism depending upon when physical activity is done during the day. Some findings suggest that morning exercise could increase insulin sensitivity better than doing it later in the day. Circadian rhythms of the body, controlling many biological processes like metabolism, may give a reason for these changes. Moreover, coordinating exercise with times to eat could improve insulin sensitivity. For example, doing physical activities after eating helps in better glucose absorption and use which assists in maintaining blood sugar levels following meals.
Putting together strong workouts with planned timing might give the biggest benefits for insulin sensitivity. For people wanting to make their metabolic health better, adding short periods of hard exercise into their schedule, particularly after eating food, can be a good plan. This method uses both the power of workout intensity and scheduling time correctly to help in improved sugar management. People can try different times in their daily routines to discover the best period for physical activity. This must align with their way of living and at the same time, maximize positive effects on insulin sensitivity.
Understanding that personal elements can change the impact of intensity and timing on insulin sensitivity is crucial. Age, sex, body structure, and present health conditions are all factors that could affect how productive exercise is in improving insulin sensitivity. For example, elderly people might need various exercise plans compared to younger ones to achieve similar enhancement in metabolic well-being. Furthermore, people who have certain health problems like obesity or diabetes might react differently to the intensity and timing of exercise. Adjusting exercise programs so they fit with these personal factors can aid in achieving better results.
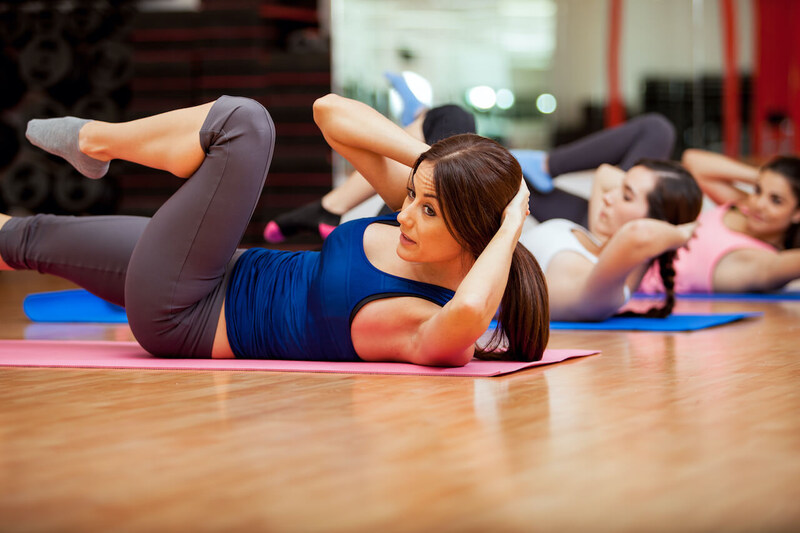

People who want to improve their sensitivity to insulin by doing exercise can follow some useful steps. First, they should do a combination of high-intensity training and moderate workouts for a balanced routine. Second, paying attention to when you work can increase the positive effects, especially if it is arranged around eating times. At last, talking with health experts or fitness professionals can assist in customizing workout plans according to personal needs. This ensures that the exercise is performed safely and effectively. By choosing wisely regarding the level of physical activity and when it's done, people have a good chance of boosting their metabolic well-being while lowering insulin resistance risks.
To sum up, the research that emphasizes the influence of workout intensity and schedule on insulin receptiveness stresses how crucial physical movement is for metabolic well-being. Knowing how these factors relate to each other can provide people with the ability to make knowledgeable choices about their exercise habits, which will eventually lead to improved health results. By concentrating both on the strength of workouts and when they do physical activity, individuals can enhance their insulin responsiveness while promoting comprehensive metabolic performance.

By Gabrielle Bennett /Oct 14, 2024

By Triston Martin/Oct 09, 2024

By Elva Flynn/Mar 17, 2025

By Madison Evans/Nov 14, 2024

By Celia Kreitner/Dec 18, 2024

By Madison Evans/Feb 07, 2025

By Madison Evans/Jan 06, 2025

By Noa Ensign/Feb 19, 2025

By Tessa Rodriguez/Dec 16, 2024

By Elena Davis/Oct 09, 2024
By Celia Shatzman/Feb 07, 2025

By Alison Perry/Feb 08, 2025