Advertisement
Oxidative stress is defined as a condition that arises when excess free radicals are compared to antioxidants in a human organism. This can also cause impairment of cells and tissues and add to several health issues. Regarding health management, it is essential to understand the balance between oxidative stress and cellular function and their interrelationships. This is how it works:
While our bodies produce some free radicals naturally, external factors can increase their levels, leading to oxidative stress.
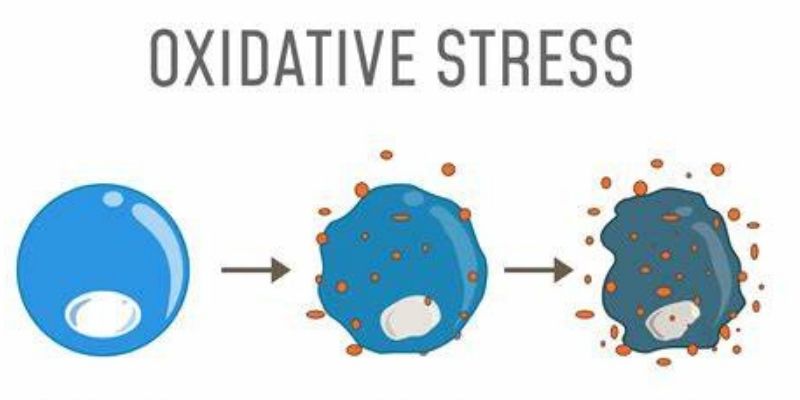
As time-rife activities of free radicals, oxidative stress can inflict damage on nearly all body systems. There are some potential effects:
Health conditions linked to oxidative stress include:
With time, due to the activities of free radicals, most of the body systems can be affected by oxidative stress, and so it can cause damage to all systems of the body. One has to take note of some possible outcomes:
Free radicals and antioxidants serve opposing functions in the human body, having unique health effects. Free radicals tend to be created within the body through mechanisms such as metabolic activity or introduced by environmental agents such as toxic substances, cigarette smoke, and even UV rays. As free radicals are incomplete molecules, they seek the missing pair of the nucleus from the nearest cell by 'picking up' an electron. Unfortunately, this chain of happenings also causes damage to cells, proteins, and even DNA, which results in oxidative stress that accelerates the aging process, along with many other diseases.
Conversely, the antioxidants defend the body against the aforementioned toxic molecules. Antioxidants, which are predominantly sourced from vibrant fruits, vegetables, nuts, and cereals, neutralize free radicals by simply giving away one of their electrons without undergoing any instability themselves. This form of protection curtails oxidative stress and offers cellular protection from damage. In a sense, antioxidants are the "repair team" of the body to contain free radicals. These two opposing forces allow the body to avoid the risks associated with old age, inflammation, and various diseases, which is why antioxidants are essential for health.
While avoiding oxidative stress entirely is impossible, there are several steps you can take to reduce its impact:
1. Include Antioxidant-Rich Foods in Your Diet
Eating foods high in antioxidants helps combat free radicals. Aim to include these in your daily meals:
Antioxidants help balance free radicals, reducing oxidative damage. A colorful, varied diet with plenty of fruits and vegetables can provide essential antioxidants.
2. Adopt a Healthy Lifestyle
Making specific lifestyle changes can further prevent oxidative stress:
3. Protect Yourself from Environmental Toxins
Reducing exposure to environmental toxins can also help manage oxidative stress:
4. Prioritize Good Sleep
Adequate sleep is essential for managing oxidative stress. Sleep supports cellular repair and balances hormones, helping your body manage free radicals. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to support these natural processes.
Managing oxidative stress requires a balanced approach that includes diet, lifestyle changes, and reducing exposure to external pollutants. By understanding the meaning of oxidative damage and focusing on anti-oxidative practices, you can take steps to protect your health.
To recap:
Prevention Tips:
Small, consistent steps toward a healthy lifestyle can help minimize oxidative stress and promote overall well-being.
Advertisement

By Triston Martin/Oct 09, 2024

By Martina Wlison/Nov 22, 2024

By Jennifer Redmond/Oct 14, 2024

By Triston Martin/Feb 28, 2025

By Madison Evans/Mar 18, 2025

By Madison Evans/Jan 06, 2025

By Susan Kelly/Feb 28, 2025

By Nancy Miller/Oct 21, 2024

By Kristina Cappetta/Dec 14, 2024

By Triston Martin/Mar 17, 2025
By Celia Shatzman/Feb 07, 2025

By Pamela Andrew/Dec 07, 2024